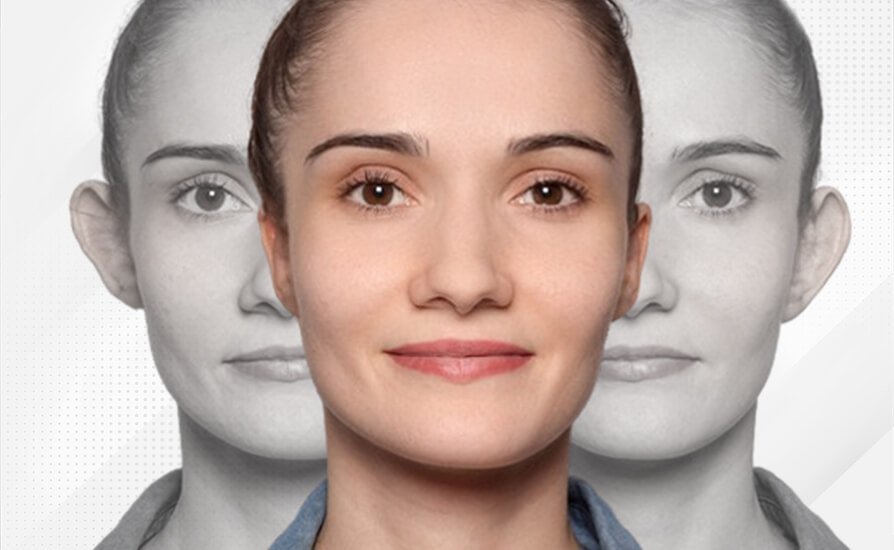
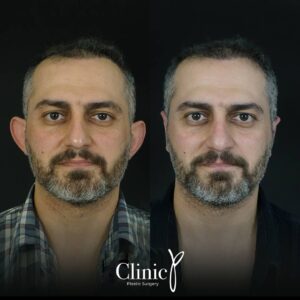
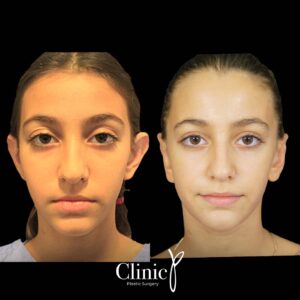
Prominent ear deformity usually arises from genetic factors. This deformity can be corrected through prominent ear surgery. Known as otoplasty in the medical field, this surgery offers a permanent solution. Among ear disorders, prominent ear issues are predominant, often leading to various psychological problems when the ears aesthetically stand out on the face. Even attempts to conceal the problem with hair might not yield significant success. Children, especially, experience heightened psychological distress due to this condition. Therefore, prominent ear surgery is recommended starting from the age of 5 or 6, when ear cartilage growth is complete. These surgeries address more than cosmetic concerns; they alleviate the psychological burden caused by prominent ears.
When is the ideal time for prominent ear surgery?
Prominent ear deformity is a widespread condition. Its congenital nature indicates a genetic influence. Ear growth and cartilage shaping continue until around ages 5 to 6. Children uncomfortable with their ear appearance might face social communication challenges. Correcting prominent ear deformity before school age prevents potential trauma. Although the surgery can be performed at any age after growth completion, experts recommend doing it before starting school.
Surgical prominent ear correction is irreversible and ensures permanent reshaping.
How is the decision for prominent ear surgery made?
After a thorough clinical examination of ear structure, a corrective approach is determined, and the surgery is planned. Symmetry might require treating both ears even if only one is deformed. Patients considering prominent ear surgery are informed about pre- and post-operative precautions. The surgeon clearly explains anesthesia type and surgical methods.
What is the process of prominent ear surgery?
Prominent ear surgery involves a discreet incision behind the ear to reshape the pinna (outer ear). Cartilage structures are reshaped and secured at the correct angle using permanent sutures. This ensures permanent ear shape correction. The operation’s significant advantage is the elimination of the possibility of recurrent prominent ear deformity. Children aged 10 to 12 usually undergo general anesthesia, while older individuals might opt for local anesthesia.
The surgery for both ears is completed in about an hour. After the procedure, the ears are bandaged. Patients treated without general anesthesia might be discharged on the same day. Bandages should remain in place for 5 days. After this period, the doctor removes the bandages and supports the ears with a tennis bandana. Following a successful operation with no noticeable scars, people experience heightened self-confidence and better embrace life.
Is prominent ear surgery risky?
The risk ratio for these operations is quite low. However, as surgical interventions, they entail potential risks such as infection, bleeding, and hemostasis. While these complications are extremely rare, patients are informed about them. Ear asymmetry is a common aesthetic concern, even before the surgery. Correcting asymmetry isn’t always straightforward. Although there are cases where initially symmetrical ears become asymmetric after the surgery, such occurrences are infrequent. Another possible outcome is ears being positioned closer to the head after the operation.
When can patients resume regular activities post-prominent ear surgery?
Male and female patients might have different experiences when returning to work and social life after the operation. Women, who often use hair bands as accessories, can quickly resume their routine. However, men may need to wait a bit before returning to regular activities since they lack this option. Hair band application proves more practical than the traditional bandage approach.